Introduction
“Are you just one click away from a cybersecurity disaster?” Hello all of our the Readers there is a big reason behind writing an article on this topic because many people want to learn it.”Cybersecurity isn’t just about protecting your data; it’s about protecting your identity, your finances, and your peace of mind. Dive into the why and how in this essential guide

“Cybersecurity isn’t just about protecting data; it’s about protecting your future. One breach can unravel your life. “Don’t wait for a breach to learn the value of protection.”
“Are you ready to rise above the cyber-threats🚀?”

*What is Cybersecurity ?
Cybersecurity is the process of protecting systems, devices, networks, and data from any type of unauthorized access or attack understand with example Imagine your phone is a secret treasure chest of your life: photos, messages, bank stuff, everything! Cybersecurity is like the invisible shield guarding it against those who seek to exploit your digital riches
**Some News and statistics of cyberattacks Globally
*According to Security Magazine, there are over 2,200 attacks each day which breaks down to nearly 1 cyberattack every 39 seconds.*
*There was an 8% increase in global weekly cyberattacks in Q2 of 2023*
*Q2 stands for second quarter Q2 – Second quarter (April – June)*
**The Top Cybersecurity Statistics of 2023 An estimated 2,200 cyberattacks per day. 255 million phishing attacks occurring in a six-month span, with over 853,987 domain names reported for attempted phishing. 2.8 billion malware attacks launched in the first half of 2022 alone.**
IC3 by the Numbers 6billion were reported in 2020. The total number of complaints received since the year 2000 is 5,679,259. IC3 has received approximately 440,000 complaints per year on average over the last five years, or more than 2,000 complaints per day.
**Victims: Report your cybercrime and empower others to stay safe**
Contact on there website
Global:
1) United Nations Office on Drugs and Crimes(UNODC):This website aggregates cybercrime data and research from across the global, supporting international law enforcement efforts. While not a direct reporting platform, your reports through national agencies might contribute to broader investigations:
2) International Criminal Police Organization (INTERPOL):Though not a direct reporting platform, INTERPOL collects cybercrime reports from member countries and facilitates international investigations. Reporting through your national agency might involve INTERPOL collaboration for major cases. https://www.interpol.int/en/Who-we-are/What-is-INTERPOL
Country-Specific
India: Cybercrime.gov.in: : – This Indian website allows reporting various cybercrimes to Indian authorities, potentially leading to police investigations and legal action within
United States: Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) – This US-based platform allows reporting various cybercrimes. However, legal action depends on contacting local law enforcement for individual cases.complain here
United Kingdom:Action Fraud: – This UK-specific platform focuses on reporting fraud, including online scams, for investigation and potential prosecution by UK authorities.complain here
Australia:Report Cybercrime:This Australian platform serves for reporting online crimes to the Australian Cyber Security Centre for investigation and potential legal action within the country.complain here
Number of incidents in December 2023: 1,351. Number of breached records in December 2023: 2,241,916,765
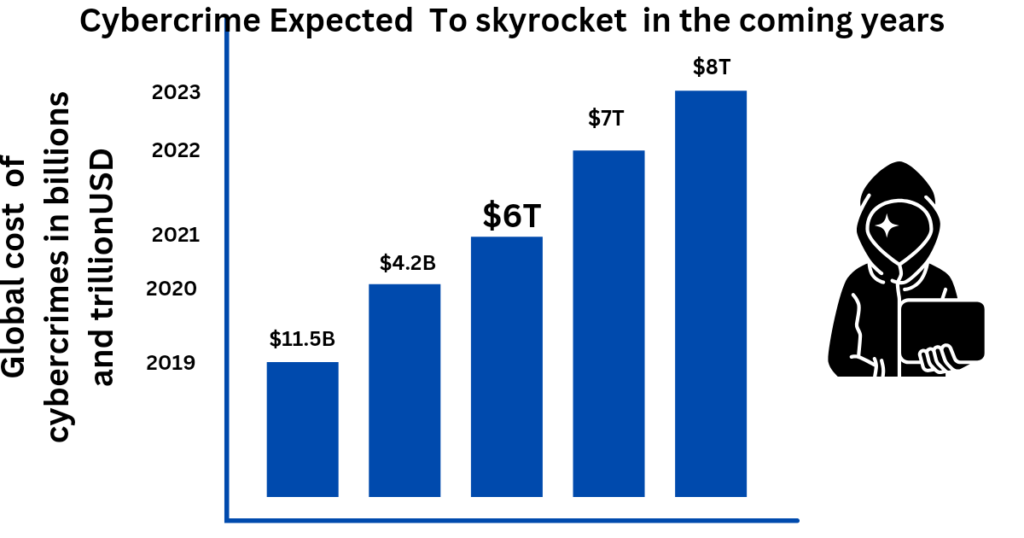
costs predicted by Cybersecurity Ventures in 2024: $9.5 trillion USD a year
The 2020 Internet Crime Report includes information from 791,790 complaints of suspected internet crime—an increase of more than 300,000 complaints from 2019—and reported losses exceeding $4.2 billion.
Some Basic Terms of Cybersecurity:
- Malware: Malicious software like viruses, worms, and Trojans that harm your device or steal data.
- Phishing: Deceptive emails or websites designed to trick you into revealing personal information
- Social Engineering: Manipulation tactics used to gain access to your data or systems.
- Zero-day Attack: Exploiting unknown vulnerabilities in software before developers can fix them.
- Firewall: Monitors and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic to block unauthorized access.
- Antivirus: Software that detects and removes malware from your device.
- Encryption: Scrambles data into an unreadable format to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication(MFA): Requires multiple forms of identification (e.g., password, code) to access data.
- Vulnerability: A weakness in a system that attackers can exploit.
- Patch: A fix for a security vulnerability.
- Digital Hygiene: Safe online practices like strong passwords and cautious clicking.
- Ransomware attacks: Hackers lock your files or data and demand payment (usually in cryptocurrency) to unlock them.
“Examples of all terms to understand easily”
- Malware: Imagine tiny digital monsters slithering through your computer’s wires, munching on your precious data like cookies.
- phishing:Imagine a sweet email like a candy-coated trap, promising free gifts or exciting news. One bite, and you’re infected with malicious code, unwittingly handing over your digital keys to the phishers. Be wary of sweet treats online, for not all sugar-coated messages are genuine
- social engineering: “oops, wrong address! Can you send your location to confirm?” (Tracks precise location for unauthorized access).
- Zero-day-attack: You follow a delicious online recipe, unaware of the secret, harmful ingredient the hacker snuck in before you started mixing. By the time your cake is out of the oven, your data is already burnt to a crisp.
- Firewall: Think of a burly bouncer at the club, checking IDs and blocking unwanted guests from entering your digital party (server)
- Antivirus: blocks access to known dangerous websites, preventing accidental exposure to malware-ridden sites
- Encryption: Imagine a magical lock for your online messages. Encryption clicks it shut, whispering secrets only you can unlock.
- Multi-Factor Authentication(MFA): Picture a double-locked treasure chest, requiring not just a key but also a secret handshake and a magical passphrase to open
- Vulnerability:Imagine a loose brick in your castle wall, a weak spot that sneaky thieves might try to exploit to sneak in and steal your treasure.
- patch: Picture a trusty repair crew quickly fixing that loose brick, sealing the weakness before attackers can take advantage.
- Digital Hygiene: Imagine your online accounts are buried gold chests, but hidden in the sand are tempting traps (phishing emails, suspicious links). Digital hygiene is like a cautious map, helping you navigate safely and avoid buried dangers.
- Ransomware attacks:The WannaCry Attack of 2017:It spread like wildfire, infecting over 200,000 computers in 150 countries.It targeted hospitals, businesses, and government agencies, causing chaos and disruption.It demanded a ransom of $300 in Bitcoin to unlock each infected machine.It exploited a vulnerability in Windows that Microsoft had patched, but many organizations hadn’t updated their systems.It even infected MRI machines forcing some hospitals to turn away patients.
Ransomware remains a significant threat. Stay vigilant with strong cybersecurity practices
1)Regular software updates
2)Cautious email and web browsing habits
3)Secure backups
4)Antivirus and anti-malware protection
5)Employee awareness training
Why cyber attacks are successful?

People mistakes is a common factor in successful cyberattacks. This can include employees falling for phishing scams, using weak passwords, or inadvertently misconfiguring security settings.
Who is Hacker?
Ethical hackers (white hats): Use their skills responsibly for good, finding and fixing security vulnerabilities, testing systems, and promoting cybersecurity awareness.
Malicious hackers (black hats): Exploit vulnerabilities for illegal or harmful purposes, like stealing data, disrupting systems, or launching cyberattacks.
Grey hats: Operate in a blurry area, sometimes exploring vulnerabilities without permission but mostly for personal knowledge or entertainment.
How Hackers get access in your system,accounts?
They try different methods to get access your account and hack your account
Brute Force Attacks: Hackers attempt to gain access by systematically trying all possible password combinations until they find the correct one.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Intercepting and potentially altering communication between two parties without their knowledge.
Credential Stuffing: Using leaked usernames and passwords from one site to gain unauthorized access to other accounts where users have reused credentials.
Phishing: Deceptive emails, messages, or websites impersonate trusted entities to trick users into revealing sensitive information.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Injecting malicious scripts into web applications that are then executed by other users’ browsers, potentially allowing attackers to steal information.
SQL Injection: Manipulating a web application’s database queries to gain unauthorized access to data or execute malicious commands.
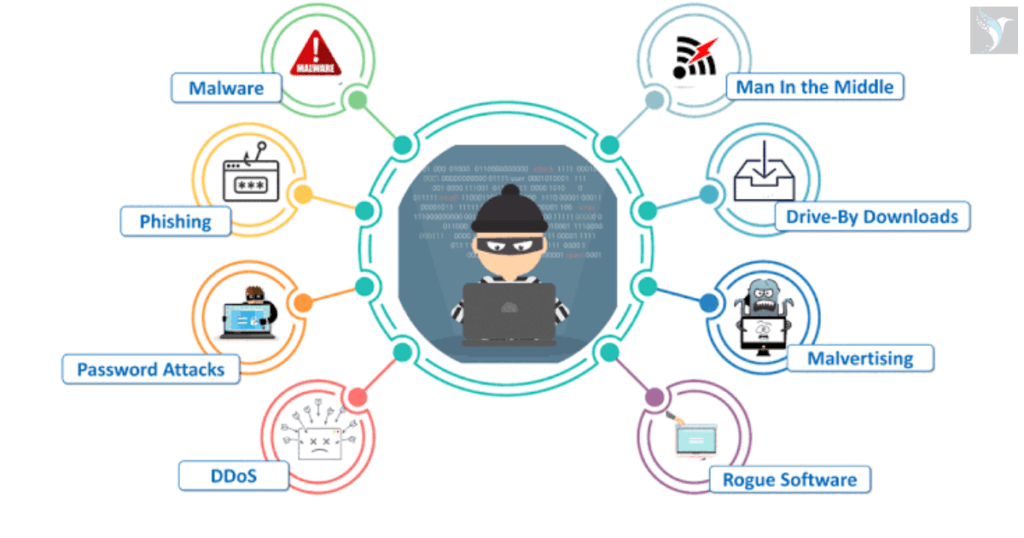
💻Some more types of cyberattacks
**DDos (Distributed Denial-of-Service):Imagine a digital mob trying to flood a website with so much traffic that it crashes. That’s a DDoS attack! Hackers use many infected devices to send overwhelming requests to a website, overloading its servers and making it inaccessible to legitimate users.
**Rogue software:Think of this as unwanted guests who crash your digital party. Rogue software is any program installed without your knowledge or consent, often bundled with legitimate software or downloaded from shady websites. It can do anything from slowing down your computer to stealing your data.
**Malvertising:Picture malicious ads with hidden hooks. Malvertising uses online advertising to spread malware or trick users into clicking on harmful links. It can disguise itself as normal ads, making it hard to spot unless you’re careful.
**Drive-By Downloads: Imagine walking past a shady alleyway and suddenly getting mugged – your data! Drive-by downloads happen when a website secretly installs malware on your computer just by visiting it. No clicking needed, just like a surprise attack in the digital world.
Rogue software can be used to launch DDoS attacks.
Malvertising can lead to drive-by downloads.
All three can steal your data and disrupt your online experience.
**Tip to protect your account from Hackers

- Craft Fortress Passwords: Ditch the “12345”s! Create unique, strong passwords for every account, using a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Consider a password manager for extra security.
- Embrace Two-Factor Firewalls: Activate two-factor authentication wherever possible. Add an extra layer of defense with a code sent to your phone or email, making it much harder for hackers to crack your defenses.
- Phishing Bait Alert: Don’t fall for phishing scams! Watch out for urgent emails or tempting deals, particularly those with misspelled words or grammatical errors. Never click suspicious links or attachments
- Social Engineering Sirens: Beware of online “friends” who request personal information or ask for security questions answers. Remember, real friends don’t need to fish for that information.
- Malware Mayhem Awareness: Be cautious about downloading files from unknown sources. Stick to trusted websites and app stores, and scan files with antivirus software before opening them
- Backup Bastion: Regularly back up your important data to a secure location, like an external hard drive or cloud storage. This ensures you can recover your information even if your account gets compromised
- Digital Hygiene Habits: Regularly review your account settings, remove unused apps, and monitor for suspicious activity. Be mindful of the information you share online, especially on social media.
- Software Sentinels: Keep your operating system and essential software updated with the latest security patches. These updates often fix vulnerabilities that hackers exploit.
- Skepticism Shields: Beware of suspicious links and downloads. Double-check sender addresses and website legitimacy. If something seems too good to be true, it probably is!
- Data Encryption Fortress: Encrypt your most sensitive data, like financial documents or personal files, to make it unreadable even if accessed by hackers.
- Security Software Guardian: Invest in robust antivirus and anti-malware software and keep it updated. Consider additional security tools like firewalls and intrusion detection systems for advanced protection.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Shield: Use a VPN when accessing sensitive data on public Wi-Fi or traveling abroad. This encrypts your internet traffic and masks your location, adding an extra layer of security.
- Cybersecurity Awareness Training: Educate yourself and your employees about cybersecurity best practices to increase overall awareness and vigilance.
**Tip to protect your smartphone ,system from apps that you download**

Use a strong firewall: This acts as a barrier between your computer and the internet, blocking unauthorized access.
Keep your operating system and software updated: This ensures you have the latest security patches and fixes.
Download apps only from trusted sources: Stick to official app stores like Google Play Store or Apple App Store and avoid third-party marketplaces.
Check app permissions before installing: Scrutinize what permissions each app requests and only allow access when necessary.
Keep apps updated regularly: Updates often patch security vulnerabilities, so update apps as soon as new versions become available.
Disable location tracking for non-essential apps: Location data can be valuable, so limit access only to apps that genuinely need it.
Turn off auto-fill features: These can be convenient, but also expose your credentials if the app gets compromised.
Review privacy settings in all apps: Understand what data each app collects and adjust settings to limit unwanted data collection.
Disable Bluetooth and Wi-Fi when not in use: These channels can be entry points for attackers, so turn them off when not needed.
FAQ ?
Q1.What is the concept of cybersecurity?
Ans.Cyber security is the application of technologies, processes, and controls to protect systems, networks, programs, devices and data from cyber attacks.
Q2.Who needs cyber security?
Ans.Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting computer systems and networks from unauthorized access or attack. Individuals, businesses, and governments must invest in cybersecurity to protect their data and assets from criminals. The importance of cybersecurity in this progressively internet-centered world is supreme.
Q3.Is cybersecurity a good field?
Ans.Besides being an increasingly in-demand profession, a career in Cybersecurity is also highly rewarding financially. Cybersecurity professionals typically earn more than other tech jobs. With the need for Cybersecurity continuing to grow, it makes this one of the most promising and well-paid careers available today.
Q4.Who is the father of cyber security?
Ans.Bob Thomas is a computer scientist who is widely regarded as the father of cybersecurity. He gained notoriety in 1971 when he created the first computer virus, called the “Creeper virus.” The virus was not malicious and was designed to demonstrate the vulnerability of computer systems.
Q5.What is AAA in security?
Ans.Authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) is a security framework that controls access to computer resources, enforces policies, and audits usage.
Q6.Is cybersecurity a future job?
Ans.As we progress in this digital age, cybercrimes are bound to grow. To combat this problem, cybersecurity job openings will rise, making it a career of the future.
Q7.Does cybersecurity have high salary?
Ans.A mid-career Cyber Security with 4-9 years of experience earns an average salary of ₹11.0 Lakhs per year, while an experienced Cyber Security with 10-20 years of experience earns an average salary of ₹26.1 Lakhs per year.
Q8.Global cost of cybercrimes by 2026?
Ans.The Global Cost of Cybercrime Statistics predict that cybercrime will cost the global economy more than 20 trillion U.S dollars by 2026,
Q9.Can I protect myself completely from cyberattacks?
Ans.(While total prevention is impossible, strong cybersecurity practices can significantly reduce the risk.)
Q10.What are the essential cybersecurity basics everyone should know?
Ans.(Strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, software updates, data backups, etc.)
Q11.What can I do if I become a victim of cybercrime?
Ans.(Report the incident to authorities, contact affected organizations, seek legal advice if necessary.)
Q12.What should I do if my social media accounts are hacked?
Ans.(Immediately change passwords, report the breach to the platform, inform contacts of the compromise, and monitor for suspicious activity.)
Q13.How can I protect my children from online threats?
Ans.(Use parental controls, filter content, talk openly about online safety, educate them on recognizing scams and suspicious behavior.)
Q14.How can I secure my online banking and financial transactions?
Ans.(Use strong passwords, avoid public Wi-Fi for financial activities, be cautious about phishing emails and fake websites.)
Q15.What career opportunities are available in the field of cybersecurity?
Ans.(The demand for cybersecurity professionals is growing, offering exciting options for those with technical skills and passion for security.)
Q16.What is the cost of cybercrimes and IPR issues?
Ans.Cybercrime incidents could cost the world nearly a trillion dollars in 2020, a 50% jump from around $600 billion in 2018.
Q17.Can cyberattacks affect my everyday life beyond stolen data?
Ans.(Yes, they can disrupt critical infrastructure like electricity or healthcare, or lead to identity theft impacting finances and credit.)
Q18.How much will the cyber crime cost in 2023?
Ans.$8 trillion USD a Year Our report provides a breakdown of the cybercrime damage costs predicted in 2023: $8 trillion USD a Year. $667 billion a Month
Q19.What is the OSI model?
Ans.The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a conceptual framework that divides network communications functions into seven layers. Sending data over a network is complex because various hardware and software technologies must work cohesively across geographical and political boundaries.
Q20.What are the 7 Layers of Cybersecurity?
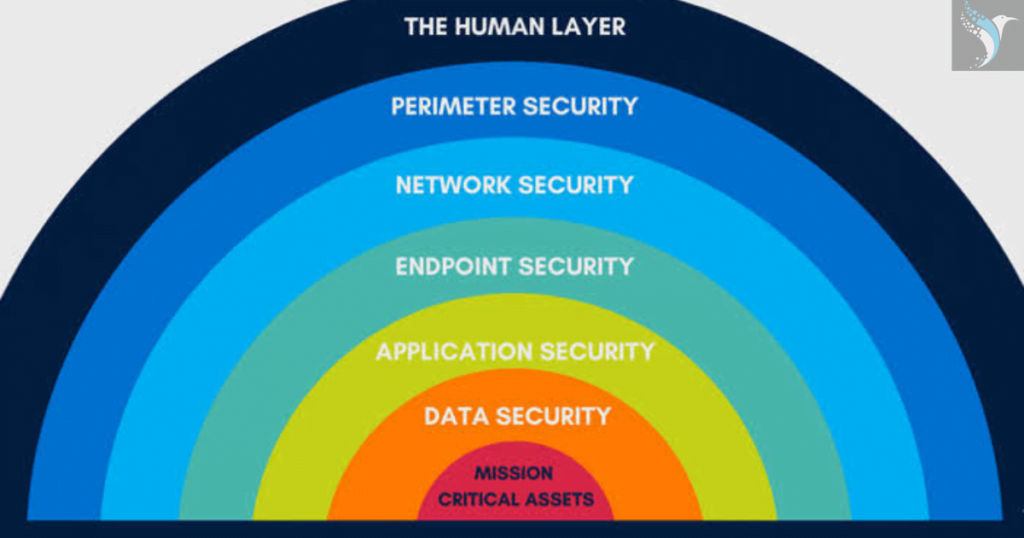
Ans.Human Layer: The human layer, often regarded as the most vulnerable layer, focuses on the human element within an organization. …Perimeter Security Layer: …Network Layer: …Application Security Layer: …Endpoint Security Layer: …Data Security Layer: …Mission-Critical Assets:
Q21.What is the meaning of WannaCry?
Ans.WannaCry is an example of crypto ransomware, a type of malicious software (malware) used by cybercriminals to extort money. Ransomware does this by either encrypting valuable files, so you are unable to read them, or by locking you out of your computer, so you are not able to use it.
Q22.What is the WannaCry case 2017?
Ans.The WannaCry ransomware attack was a worldwide cyber-attack which took place in May 2017. The cyber-attack targeted PCs running Windows. The attackers encrypted data and demanded a ransom, if this was not paid the group threatened to release data/information
Q23.What are the 5 types of Cybersecurity
Ans.
1. Critical Infrastructure Security:This focuses on protecting essential services like power grids, hospitals, transportation systems, and financial institutions. Cyberattacks on these systems can have widespread consequences, disrupting entire nations. Security measures include:
Physical security
Network security
Industrial Control System (ICS) security
2. Application Security:This involves securing software applications from vulnerabilities that hackers can exploits It encompasses a range of practices, including:
Secure coding Practice
Regular vulnerability scanning
Access control
3. Network Security:This safeguards your computer networks from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other threats. Security measures include:
Firewall
Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS)
Data encryption
Network segmentation
4. Cloud Security:This protects data and applications stored in cloud computing environments. Security measures include:
Shared responsibility model
Data encryption
Access control
Incident response plans
5. Internet of Things (IoT) Security:This protects internet-connected devices like smart homes, wearables, and industrial sensors from cyberattacks. Security measures include:
Secure device design
Regular firmware updates
Strong authentication and authorization
Q24.What is the full form of cyber?
Ans. CYBER Stands For : Changing Yesterdays Behavior For Enhanced Results. cyber- a combining form meaning “computer,” “computer network,” or “virtual reality,” used in the formation of compound words (cybertalk; cyber art; cyberspace) and by extension meaning “expressing visions of the future” (cyberfashion).
Q25.Which is called cyber crime?
Ans.Cybercrime is any criminal activity that involves a computer, network or networked device. While most cybercriminals use cybercrimes to generate a profit, some cybercrimes are carried out against computers or devices to directly damage or disable them.
Network segmentation
“In the ever-evolving digital landscape, vigilance is our strongest defense. Stay informed, stay secure, and let’s build a safer future together.”
“Empower yourself with knowledge. Cybersecurity is not just for IT experts; it’s a responsibility we all share. Take control of your online safety and become a force for good in the digital world.”
“Share this article and spread awareness about the importance of online safety.”