What is Blockchain?
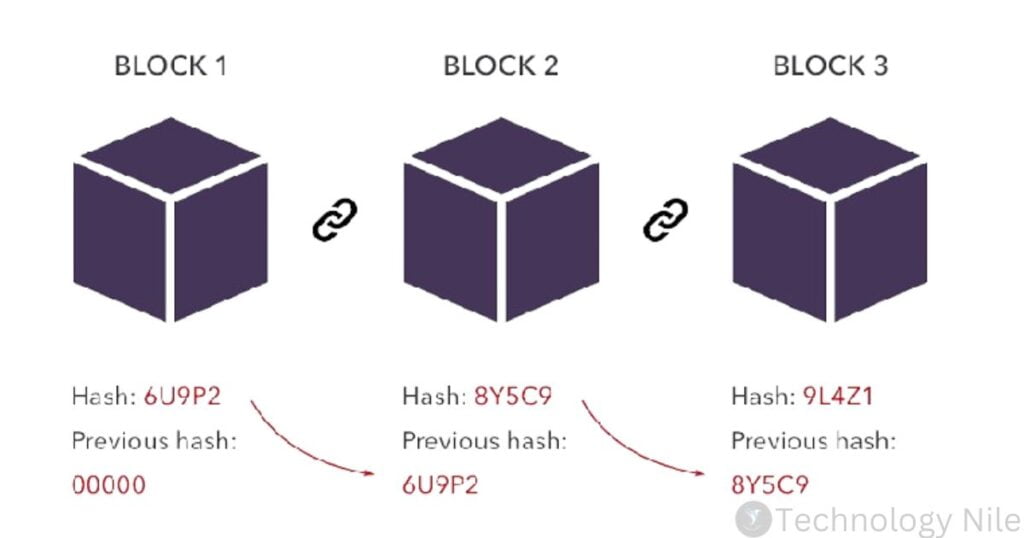
Blockchain Collects information in groups and the groups are called Blocks. each blocks has limited storage capacity. That’s why when a block is filled, it connects to the previously filled blocks.When a new block is created, it includes a unique code (hash) referencing the previous block’s hash. Tampering with any block would invalidate its hash and disrupt the entire chain, making it easy to detect.
How Blockchain Works?
Blockchain can be imagined as a public record-keeping system for transactions. Instead of a central authority controlling the information, it’s spread across a network of computers. Transactions are grouped into blocks, containing details like timestamps and involved parties. Each block is encrypted with a unique code (hash) based on its contents and the hash of the previous block. This creates a chain where tampering with any block would alter its hash and disrupt the entire chain, making it easy to detect. This distributed ledger system with strong cryptography ensures secure, transparent, and verifiable recording of transactions without a central body for control.
Example – Imagine you’re sending money to a friend. Traditionally, this would involve going through a bank. The bank would update its ledger to reflect the transfer of funds from your account to your friend’s account.With blockchain, there’s no central bank. Instead, the transaction is broadcast to a network of computers. These computers verify the transaction and then add it to a block. This block is then linked to the previous block, and so on, forming a chain of blocks – the blockchain.
Key Takeaways
- Blockchain can help to reduce fraud and errors.
- Blockchain can provide a clear audit trail for transactions.
- Blockchain can automate some processes, which can save time and money.
What is Hash?
Blockchain relies on special algorithms called hashing functions to secure the information stored within.Hashes act as the building blocks for blockchain’s security and transparency. They provide a tamper-proof way to store and verify data, making blockchains a powerful tool for various applications.
How Hashing Algorithm Works?
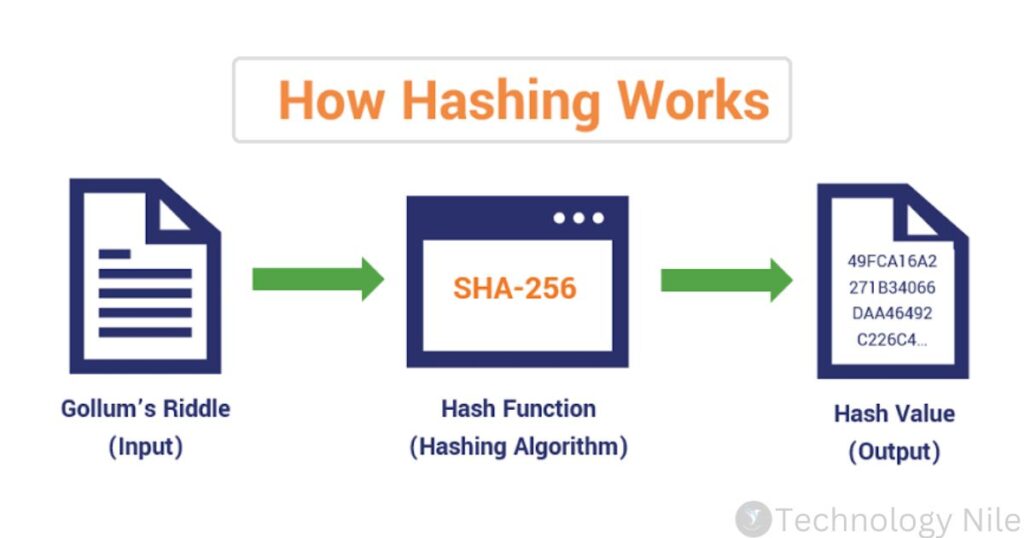
It scrambles and mixes the data up using complex mathematical operations, churning out a unique string of characters called a hash. This hash acts like a digital fingerprint for the original data.
Block Hashes: Each block in a blockchain stores data (usually transactions) along with a hash generated from that data. This hash is like a summary of the block’s content.
Chaining the Blocks: The magic happens when the current block also includes the hash of the previous block in its data. This creates a chain-like structure where each block is cryptographically linked to the one before it.
Hashing algorithms act as the backbone for blockchain security. They ensure data integrity and immutability, making blockchains a reliable and tamper-proof way to record information.
Candlestick Charts complete tutorial – click here